Exploring RavenDB
Published: 2025-11-21
I recently came across RavenDB while exploring modern NoSQL databases, and I was impressed by what it offers. RavenDB is a document-oriented database with some unique features that set it apart from other NoSQL solutions, and we’re seriously considering adding support for it in a future version of DbGate.
What is RavenDB?
RavenDB is a NoSQL document database designed for .NET applications, though it works perfectly with any platform. What makes RavenDB interesting is its focus on ease of use and developer productivity. Unlike many other NoSQL databases, RavenDB includes features like:
- ACID transactions - full transaction support across documents
- Built-in indexes - automatic and custom indexes for fast queries
- Document relationships - include and reference related documents easily
- Time series data - native support for time-series data storage
- Full-text search - integrated search capabilities without external tools
How to Try RavenDB Easily
Getting started with RavenDB is surprisingly simple. The easiest way to try it is using Docker:
docker run -d -p 8080:8080 -p 38888:38888 ravendb/ravendb
Then open your browser at http://localhost:8080 to complete the setup wizard. You can choose to run in unsecured mode for development, which makes it perfect for quick testing.
Alternatively, RavenDB offers a cloud version at cloud.ravendb.net where you can get a free database instance without any installation.
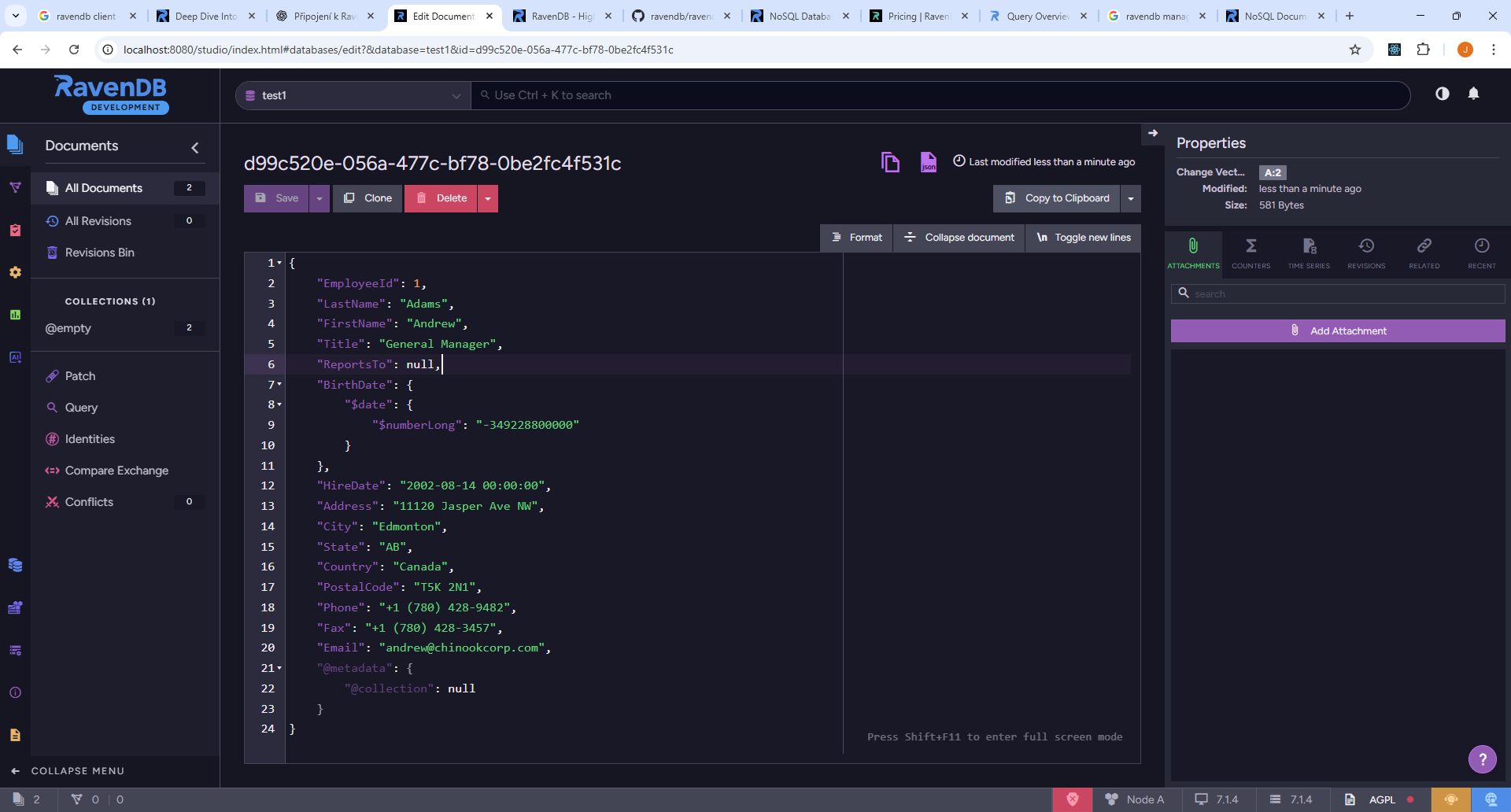
RavenDB Management Studio
RavenDB comes with a built-in web-based management studio that provides a user-friendly interface for managing your databases. The studio allows you to:
- Create and manage databases - Easily create new databases and manage existing ones.
- Define indexes - Create and manage indexes to optimize query performance.
- Monitor performance - View detailed statistics and performance metrics.
- Query data - Use a rich query editor with support for LINQ and RQL.
Let us know if you want RavenDB support in DbGate
Although RavenDB has its own Manegement Studio, which is automatically included with the database, we understand that some users prefer to manage all their databases from a single tool like DbGate. Of course, some operations like imports, exports, or advanced queries might still be better handled in DbGate.
If you’re using RavenDB and would like to see it supported in DbGate, please let us know! You can:
- Use our discussion forum
- Contact us through our email
- Share your use case - tell us how you’re using RavenDB
- Vote for the feature - let us know this is important to you
User feedback is crucial in helping us decide which databases to prioritize for future releases.
Conclusion
RavenDB is an interesting player in the NoSQL landscape, offering a nice balance between flexibility and features. If you’re working with .NET or need a document database with strong consistency guarantees, it’s definitely worth checking out. While we don’t currently support it in DbGate, we’re keeping a close eye on it and may add support in the future based on user interest.
What do you think? Would RavenDB support be valuable for you? Let us know!